What Is Power Line Communication (PLC)?
[Update Date: 17 July 2024]
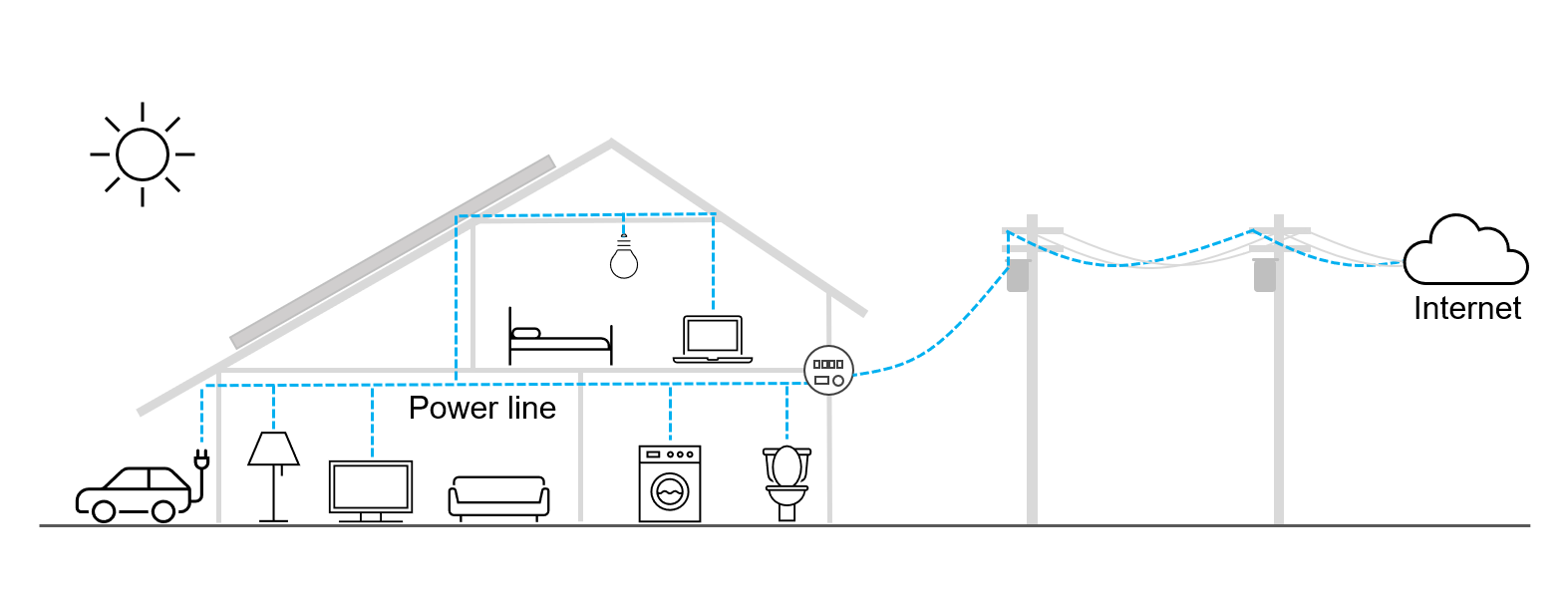
Power Line Communication (PLC) is a data transmission technology using existing power lines.
Using existing cables as a transmission line can build a network in a short construction period and at a low cost.
Power and data can be transmitted with a single cable, no new wiring of communication cable will be needed in a network.
PLC Technology – How Does It Work?
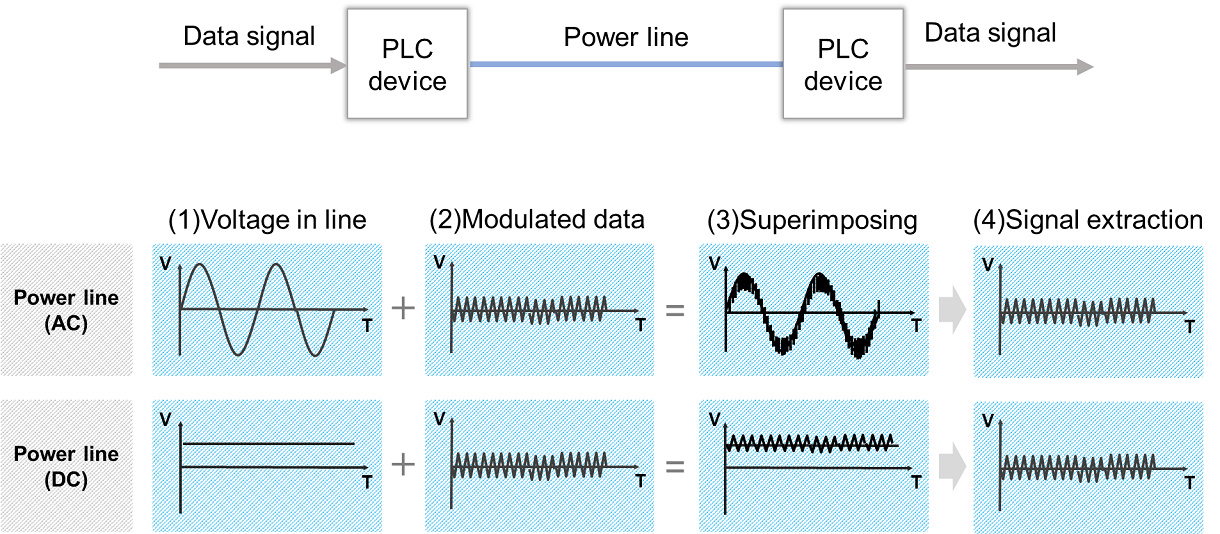
The figure above depicts the fundamental principle of Power Line Communication (PLC).
During data transmission between two devices, the transmitter modulates the data and superimposes the modulated signal onto the AC or DC power supply voltage.
The receiver then extracts the data by separating the power supply voltage and the modulated signal using a filter and demodulating the modulated signal.
PLC technology is not limited to AC power lines; it can also be employed for data transmission on DC power lines, such as those found in storage batteries, photovoltaic systems, and electric vehicle charging stations.
Positioning of PLC Network in IoT System
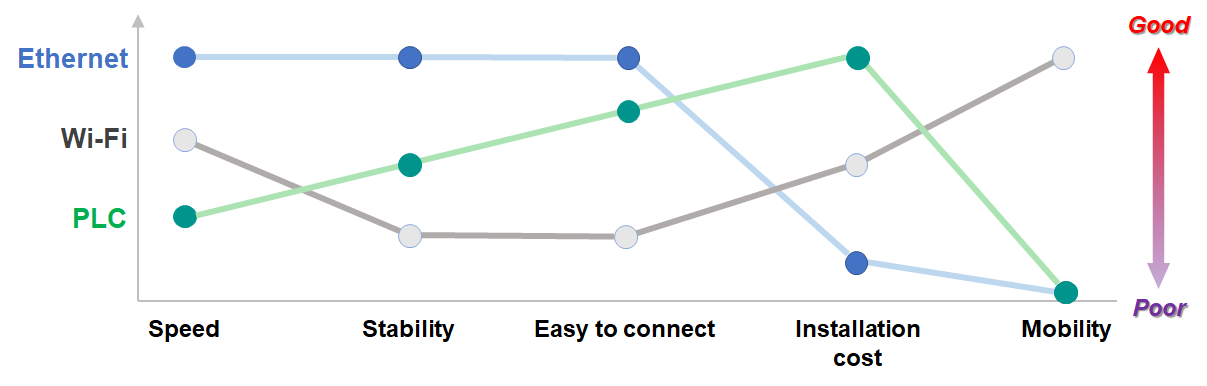
Advantages and Disadvantages Compared to Wi-Fi and Ethernet
Power Line Communication (PLC) stands as a viable alternative to Wi-Fi and Ethernet networks, offering a unique blend of performance, cost-effectiveness, and reliability.
Let's delve into a comparative analysis of PLC against these established networking technologies.
- Performance – PLC delivers moderate performance, catering to the needs of most Internet of Things (IoT) applications. While it may not match the speeds of Ethernet, it surpasses Wi-Fi in terms of stability and resistance to interference.
- Cost-effectiveness – PLC stands out as a budget-friendly option compared to Ethernet cabling installations. The elimination of the need for extensive cabling infrastructure significantly reduces overall network setup costs.
- Reliability – PLC technology is inherently resistant to interference from walls, floors, and other obstacles, ensuring a stable and consistent connection. This makes it particularly suitable for applications in challenging environments where Wi-Fi signals may be weak or unreliable.
- Security – PLC networks offer enhanced security compared to traditional Wi-Fi networks, as the power lines within a building act as a secure medium for data transmission.
- Hybrid Networks – For those seeking the best of both worlds, a hybrid network combining PLC and Wi-Fi can be an optimal solution. This approach leverages the strengths of each technology, utilizing PLC for backbone connectivity and Wi-Fi for wireless access points.
Compelling Choice for IoT
PLC emerges as a compelling choice for establishing reliable, cost-effective, and secure networks, particularly in IoT applications.
Its ability to overcome Wi-Fi's limitations and offer a more affordable alternative to Ethernet makes it a versatile solution for a wide range of networking needs.
Whether employed independently or integrated into hybrid networks, PLC is poised to play an increasingly significant role in the ever-evolving landscape of connectivity.
Types of PLC Technology
| Frequency Band |
Technology Name |
Frequency Range |
Transmission Distance |
Physical Layer Speed |
International Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Narrowband | G3-PLC | < 148.5 kHz (EU) < 490 kHz (FCC) |
Long | < 280 kbps[1] | ITU-T G.9901 ITU-T G.9903 IEEE 1901.2 |
| PRIME | < 1.0 Mbps[2] | ITU-T G.9901 ITU-T G.9904 IEEE 1901.2 |
|||
| Mid-band | HPLC | 0.7 - 12 MHz | Middle | 150 kbps to 10 Mbps[3] | IEEE 1901.1 |
| Broadband | Nessum WIRE | 0.06 - 100 MHz(*) | Long to Short | 7.8125 to 860 Mbps[4] | IEEE 1901 IEEE 1901c ITU-T G.9905 |
| G.hn | 2.0 - 80 MHz | Short | < 1.5 Gbps[5] | ITU-T G.9960 ITU-T G.9961 ITU-T G.9962 ITU-T G.9963 ITU-T G.9964 |
|
| HomePlug | 1.8 - 86 MHz | < 1.3 Gbps[6] | IEEE 1901 |
Narrowband PLC
G3-PLC
G3-PLC is a narrowband PLC technology managed by G3 Alliance. The related standards are G.9901, G.9903, and IEEE 1901.2. It can offer physical data rates up to 280 kbps in the FCC band.
PRIME
PRIME (PoweRline Intelligent Metering Evolution) is a narrowband PLC technology managed by PRIME Alliance. The related standards are G.9901, G.9904, and IEEE 1901.2. The physical data rate is up to 1.0 Mbps in the FCC
Mid-Band PLC
HPLC
HPLC is a mid-band PLC technology intended for smart meters, smart traffic lights, etc. The related standard is IEEE 1901.1. The physical data rate is up to 10 Mbps.
Broadband PLC
Nessum WIRE
Nessum WIRE is a broadband PLC technology of long-range/high-speed wired communication using any wire, not limited to power lines, such as twisted-pair cables, coaxial cables, etc. This technology is managed by Nessum Alliance. The related standards are IEEE 1901 and G.9905. The physical data rate can be changed flexibly from 7.8125 Mbps (for long-range mode) to 860 Mbps (for high-speed mode).
G.hn
G.hn (Gigabit Home Network) is a broadband PLC technology managed by Home Grid Forum. The related standards are G.9960, G.9961, G.9962, G.9963, and G.9964. The physical data rate is up to 1.5 Gbps.
HomePlug
HomePlug was a broadband PLC technology managed by HomePlug Powerline Alliance. The Alliance announced in October 2016 that it would wind down its activities, and as of December 2021, the Alliance website (http://www.homeplug.org/) has been closed. The related standard is IEEE 1901. The physical data rate is up to 1.3 Gbps.
For a more in-depth exploration of Broadband PLC, please refer to the following comprehensive article:
What Is Broadband Over Power Lines (BPL)?
Applications – Where Is Power Line Communication Used?
PLC technology is widely used to reduce network construction costs and empowers Smart Building, Smart Factory, Smart Grid, and Smart City.
Some examples of fields where this technology can be applied below:
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
- Micro-inverter
- Storage battery
- Smart street light
- Lighting control
- Automotive
- Industrial robot
Advanced Use of PLC Technology
As the name suggests, PLC technology was born as a technology to communicate using power lines. In addition, this technology could also be applied to other types of cables such as coaxial and twisted-pair cables. This development has expanded the range of fields in which PLC technology can be applied.
For example, in systems controlled by legacy, low-speed wired communications such as RS485/RS232C, PLC can significantly upgrade communication performance while using the infrastructure as is. In particular, high-speed communication in Broadband PLCs such as Nessum WIRE and G.hn is effective.
Key Facts To Remember
As the Internet of Things (IoT) expands, the communication environments and required communication performance are becoming more diverse. A single communication method does not necessarily solve all problems.
By adding the option of PLC to widespread communication methods such as Wi-Fi, Ethernet, and RS485/RS232C, each technology can complement the other's challenges/weaknesses and provide customers with the optimal network solution.
Here are key benefits of PLC for your IoT network:
- Short-period and low-cost network construction: PLC utilizes existing cables (AC or DC power lines) for data transmission, minimizing infrastructure costs.
- Performance tailored to needs: PLC offers a range of options (Narrowband, Mid-band, Broadband) with varying transmission speeds and distances, allowing you to choose the most suitable solution for your specific application.
- Cost-effective alternative: Compared to Wi-Fi and Ethernet, PLC provides moderate data transfer speeds (sufficient for most IoT applications) at a lower cost.
- Hybrid network potential: Combining PLC with Wi-Fi can leverage the strengths of both technologies, offering a robust and adaptable network solution.
By considering these advantages, PLC can be a valuable addition to your IoT connectivity strategy.
Learn more about Nessum WIRE
Reference
[1] Specifications & User Guidelines
[2] Specification for PoweRline Intelligent Metering Evolution v1.4
[3] What Is PLC-IoT? How Does PLC-IoT Work? – Huawei


![[Past Event] Presenting Nessum Technologies to the World at AHR Expo 2026!](https://nessum.org/dcms_media/image/AHR-Expo-2026.png)
