Future-Proofing Smart Grid Communication: The Potential of Next-Generation Power Line Communication Technology “Nessum WIRE”

Table of Contents
- A Turning Point for Communication Infrastructure in Smart Grids
- What India’s Experience Reveals―Practicality and Challenges of PLC
- Learning from European Examples―How Nessum WIRE Addresses Smart Grid Challenges
- Core Technologies and Competitive Advantages of Nessum WIRE
- Building a Future-Oriented Smart Grid with Nessum WIRE
A Turning Point for Communication Infrastructure in Smart Grids

Driven by the global initiatives for decarbonization and the widespread adoption of renewable energy, smart meters and Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) are rapidly being deployed as foundational elements for both Green Transformation (GX) and Digital Transformation (DX). Among these components, communication infrastructure plays a critical role—not merely as a technical layer, but as a strategic enabler for operational efficiency, revenue growth, and long-term sustainability.
Traditionally, smart grid communications have used technologies such as Narrowband Power Line Communication (NB-PLC), a type of PLC, as well as cellular networks (4G/LTE) and sub-GHz wireless solutions. However, these approaches present varying challenges in terms of performance, cost, and technological sustainability. As a result, more companies are now exploring alternatives for next-generation communication platforms. One technology gaining significant attention in this context is "Nessum WIRE", an advanced Broadband PLC solution.
In this article, we will examine PLC and its next-generation evolution—Nessum WIRE—through actual deployments in regions such as India and Europe. We will assess its practicality and ability to address existing challenges, while highlighting its technical advantages compared to other communication technologies. Furthermore, we will explore its potential as a flexible, cost-efficient communication backbone—not only for smart meters and AMI, but also for applications such as EV charging and renewable energy integration. Our goal is to provide strategic insights for companies seeking to build mid- to long-term roadmaps in this rapidly evolving domain.
What India’s Experience Reveals: Practicality and Challenges of PLC
In February 2025, the IEEE Industry Connections Working Group[1] published the white paper summarizing pilot projects, deployment cases, challenges, and prospects of PLC adoption in India.
Until now, smart meters and AMI systems in India have primarily relied on cellular communication based on 4G networks. However, due to mobile network operators’ policies on maintaining 4G infrastructure and the generational shift from 4G to 5G, there is a looming risk that these networks will become non-operational within a few years, requiring additional investment for network reconstruction. Furthermore, deploying cellular-based solutions in remote areas such as mountainous regions and rural communities—where 4G coverage is limited—remains a significant challenge.
Against this background, the white paper was issued to reassess PLC and explore its potential. One notable example highlighted in the document is the Tripura State Electricity Corporation Limited (TSECL)[2], which successfully connected approximately 43,000 smart meters using PLC. This initiative delivered concrete benefits, including reduced meter reading costs, maximized revenue collection, and effective prevention of electricity theft. Similarly, a pilot project conducted by the Central Power Research Institute (CPRI)[3] demonstrated that NB-PLC-based Automatic Meter Reading (AMR) can serve as a viable communication method independent of mobile network operators.
These cases emphasize PLC’s practicality as a communication technology utilizing existing power line infrastructure. However, traditional PLC still faces challenges such as susceptibility to noise from peripheral equipment, lower data rates with limited bandwidth, and security concerns. These limitations highlight the need for migration to advanced next-generation technologies.
Learning from European Examples: How Nessum WIRE Addresses Smart Grid Challenges
This section highlights practical examples from Europe that demonstrate the effectiveness of the next-generation PLC technology, Nessum WIRE.
Power Plus Communications AG (PPC)[4]
In the early stages of Germany’s smart meter rollout, LTE (4G) was the primary communication method. However, several issues emerged: poor signal strength for meters installed underground, dependency on mobile network operators, and increasing SIM management costs.
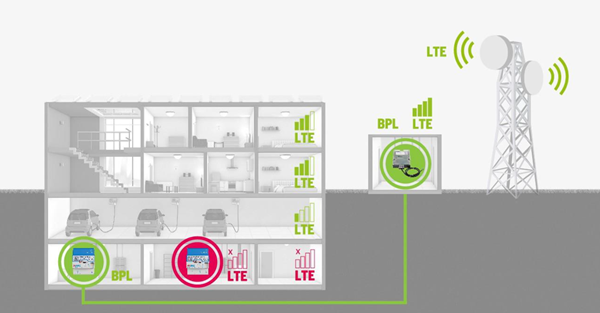
[Source] Nuremberg relies on BPL for its Smart Meter rollout
To address these challenges, PPC utilized Broadband PLC (BPL) technology compliant with IEEE 1901-2010, redefining the existing low-voltage power grid as a communication infrastructure. According to PPC’s estimates, as the number of smart meter gateways (SMGW) increases, BPL becomes more cost-efficient compared to LTE.
Building on this success, PPC adopted Nessum WIRE, compliant with IEEE 1901-2020. By combining flexible bandwidth adjustment with multi-hop technologies, Nessum WIRE overcame BPL’s traditional limitation of communication range. With support for connecting over 1,000 devices, Nessum WIRE is now recognized as one of the most future-ready BPL technologies for smart grids.
Explore PPC's Use Case
GE Vernova Inc.[5]
GE Vernova has also integrated Nessum WIRE into its communication platform, MDS™ Orbit PowerNet. By utilizing medium-voltage (MV) and low-voltage (LV) distribution networks, Nessum WIRE enables high-speed communication that traditional NB-PLC could not achieve and supports advanced AMI and SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems.
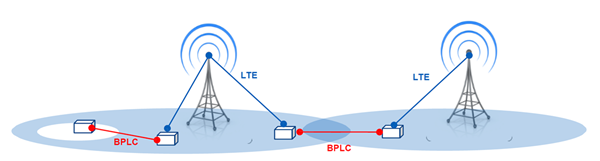
[Source] Critical Infrastructure Communication - Nessum Europe Day on Nov. 2024
In regions where cellular communication (4G/LTE) remains dominant, combining cellular networks with BPL can build a highly available and redundant network, providing coverage extension and failover capabilities.
Explore GE Vernova's Use Case
Multi-vendor Interoperability
In March 2025, both companies conducted a joint demonstration confirming interoperability across different chipsets. Nessum WIRE supports multi-vendor chipset supply, enabling utilities to avoid vendor lock-in and ensure stable procurement. This achievement ensures that Nessum WIRE supports flexible network expansion—significantly enhancing reliability and future scalability in deployments.

Core Technologies and Competitive Advantages of Nessum WIRE
Nessum WIRE is a next-generation wired communication technology that utilizes existing power lines to build long-distance, wide-area networks—while maintaining the benefits of Broadband PLC (BPL)[6][7].
This technology achieves an extended communication range by concentrating signal energy in lower frequency bands, optimized for the characteristics of the transmission line. Additionally, it supports large-scale networks with up to 1,024 devices per master and automatic multi-hop relaying of up to 10 hops. Through the original signal processing technology, Nessum WIRE enables flexible bandwidth adjustment, realizing higher speeds (from several to tens of Mbps) compared to NB-PLC, while achieving longer communication distances (from several to tens of kilometers) than conventional BPL.
Moreover, Nessum WIRE continues to evolve with advanced features such as robust error correction and channel estimation for improved noise immunity, as well as enhanced security through AES 128-bit encryption and support for IEEE 802.1X authentication.
For a detailed comparison with other PLC technologies, please refer to this article.
Building a Future-Oriented Smart Grid with Nessum WIRE
There is no doubt that Nessum WIRE stands out as one of the most promising options for the next-generation communication infrastructure in smart grids.
- Freedom from dependency on mobile network operators
- Long-term technological sustainability and international standardization
- Stable component procurement enabled by multi-vendor chipset support, reducing supply chain risks and avoiding vendor lock-in
- Proven deployment benefits in Europe
- Versatile applications across smart meters, AMI, EV charging, and renewable energy integration
Companies should consider these factors when shaping mid- to long-term strategies. Nessum WIRE has the flexibility to maximize existing infrastructure while preparing for the future of smart cities and distributed energy systems. Its balance of high-speed and long-distance communication, enhanced robustness, and advanced security features make it an indispensable component for the digitalization of power grids.
Now is the time to evaluate a migration toward a sustainable and flexible communication backbone. Nessum WIRE could be the first step toward that future.
Let’s explore how Nessum can offer benefits to your business.
Reference
[1] Establishment of Power Line Communication (PLC) Test Beds in India | IEEE SA
[2] Official Website | Tripura State Electricity Corporation Limited
[3] Home | CPRI
[4] Power Plus Communications AG | Power Plus Communications AG
[5] GE Vernova | The Energy of Change


![[Past Event] Presenting Nessum Technologies to the World at AHR Expo 2026!](https://nessum.org/dcms_media/image/AHR-Expo-2026.png)
